Locally adapted guidelines should be imple-. Describe the key principles in diagnosing and managing influenza in hospitalized patients LEARNING OBJECTIVES.
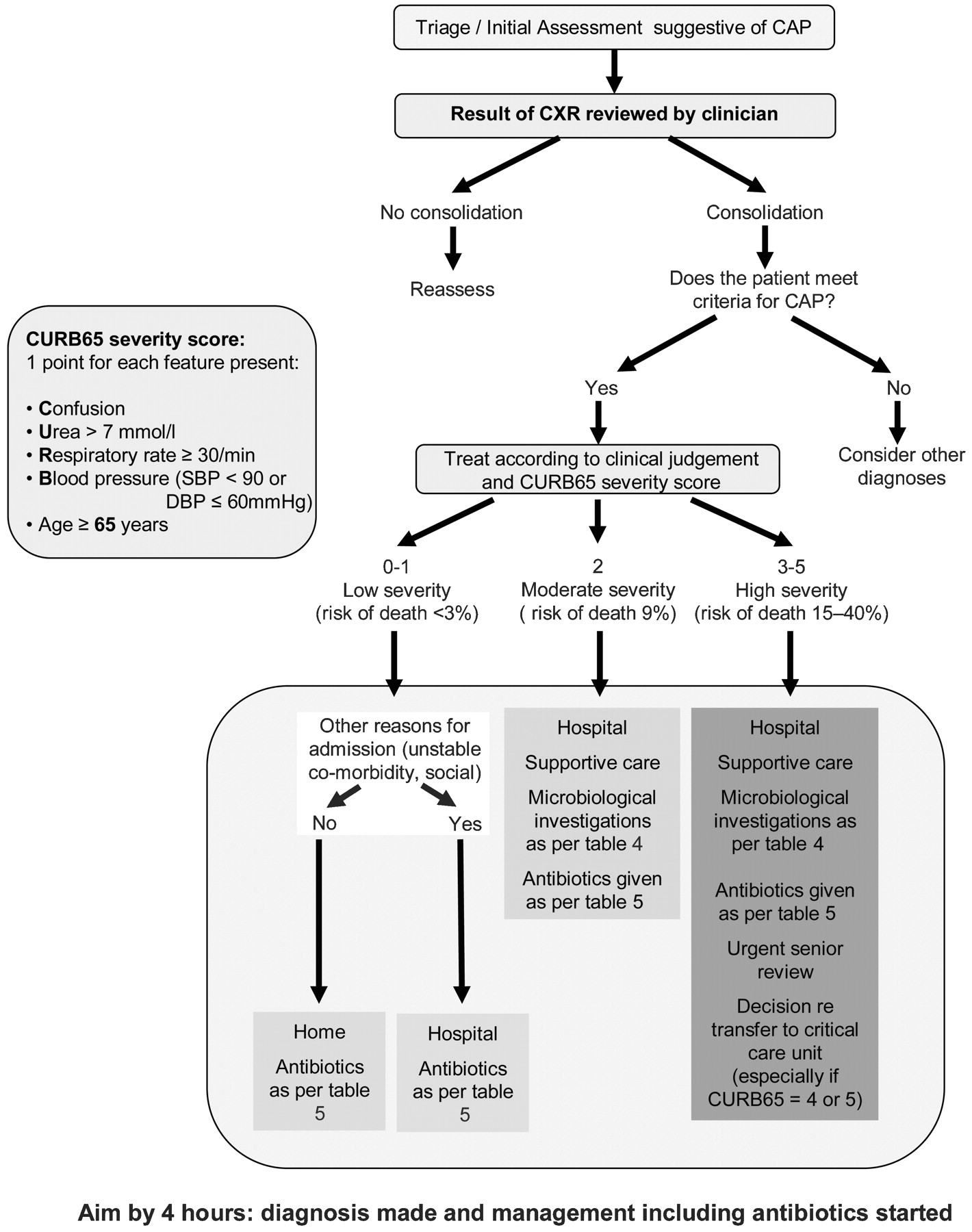 Bts Guidelines For The Management Of Community Acquired Pneumonia In Adults Update 2009 Thorax
Bts Guidelines For The Management Of Community Acquired Pneumonia In Adults Update 2009 Thorax
H We suggest no routine use in severe CAP.
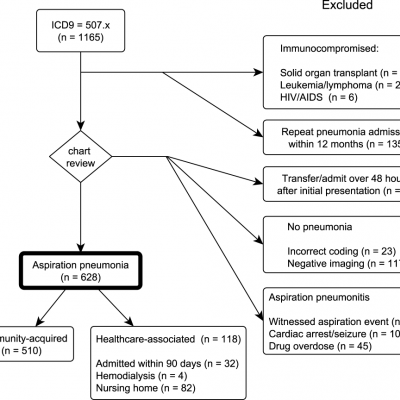
Aspiration pneumonia treatment guidelines idsa. The last CAP guidelines were released in 2007. At the outset the IDSA guidelines strongly rec-ommend a chest radiograph for all suspected CAP patients to confirm the presence of pneumonia. In addition to clinical judgement we.
Complications of disease include lung abscess and empyema. A multidisciplinary panel conducted pragmatic systematic reviews of the relevant research and applied Grading of Recommendations Assessment Development and Evaluation methodology for clinical. The term aspiration pneumonia should be reserved specifically for pneumonitis resulting from aspiration of oropharyngeal or gastric contents.
However certain other patients whose conditions are included in the designation of HCAP are better served by management in accordance with CAP guidelines with concern for specific pathogens. Pneumonia and should be treated according to the HCAP guidelines. Several more recent studies did not find a major role for anaerobes in etiology.
Infection due to inhalation of oropharyngeal secretions colonized by pathogenic bacteria. We recommend not routinely using corticosteroids in nonsevere CAP. This is typically due to impairment of the clearance defenses eg depressed sensorium glottic closure or cough reflex.
Challenges remain in distinguishing aspiration pneumonia from. O A proportion of patients 2025 may develop bacterial pneumonia 4872 hours after an aspiration event. Strength of recommendation and.
Diagnosis is based on clinical signs or symptoms of pneumonia in a person with a history or risk factors for aspiration. Term reserved for cases in which a large amount of aspirated material associated with recognizable pulmonary sequelae vs. Sputum or tracheal Gram stain reveals mixed flora.
In the more than 10 years since the last American Thoracic SocietyATSInfectious Diseases Society of America IDSA community-acquired pneumonia CAP guideline there have been changes in the process for guideline development as well as generation of new clinical data. If no or minimal improvement and bacterial pneumonia is suspected treat for 57 days. Patients with aspiration events not treated initially with no improvement in 4872 hours.
L We endorse the Surviving Sepsis Campaign recommendations on use in CAP and refractory shock. Radiographs are particularly valuable for CAP pa-tients admitted to the hospital because they provide Figure 1. Intravenous vancomycin or linezolid for 7 days.
Why does this matter. Implementation of Guideline Recommendations 1. Infection usually involves the dependent lung lobe.
Fifth the new guidelines recommend against routinely adding coverage against anaerobes in suspected aspiration pneumonia unless empyema or lung abscess is present. ATS and IDSA agreed on moving from the narrative style of previous documents to the Grading of Recommendations. Algorithm for CAP treatment.
Pathogens for CAP by age group16 Figure 2. Treatment What are the IDSA and ATS guidelines for treatment of aspiration Tб khГіa. Q10 Aspiration pneumonia.
List the major updates to the new IDSA CAP guidelines 2. Refer to Pediatric Antimicrobial Dosing Guideline for further guidance on dosing in children and Neonatal Dosing Guideline for infants 1 month of age. In March 2007 the Infectious Diseases Society of America IDSA and the American Thoracic Society ATS issued a consensus guidelines document on the management of community-acquired pneumonia CAP 1.
Therefore adding anaerobic coverage might cause harm without added benefit. Q67 Clinical prediction rules. Microaspiration which is initial step in pathogenesis of.
Reduce blood cultures ditch procalcitonin reduce anaerobic coverage for aspiration no more empiric corticosteroids no more HCAP and knee jerk broad spectrum antibiotics - these are some of the community acquired pneumonia CAP updates since 2007. IDSA Clinical Practice Guidelines are developed by a panel of experts who perform a systematic review of the available evidence and use the GRADE process to develop evidence-based recommendations to assist practitioners and patients in making decisions about appropriate health care for specific clinical circumstances. Aspiration Pneumonia The causative agents in aspiration pneumonia have shifted from anaerobic to aerobic bacteria.
M We suggest no routine use in influenza PNA. This document provides evidence-based clinical practice guidelines on the management of adult patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Recognize the appropriate antibiotic regimens and duration of therapy for hospital-acquired pneumonia 3.
Consult a pediatric pharmacist for individualized renal or hepatic dose adjustment. The 2016 IDSA and American Thoracic Society ATS guidelines for the management of MRSA pneumonia recommends the following for treatment strategies. The document includes important advances and uni-fies the previous guidelines released separately by the two societies.
Often similar organisms to community-acquired pneumonia. Construct an antibiotic plan to treat aspiration pneumonia 4.