The changes will also allow prescribers such as doctors and nurse practitioners to implement best-practice opioid prescribing for people living with. The three areas of focus in the guideline include.
 Opioid Prescribing Is Still High And Varies From County To County Cdc Online Newsroom Cdc
Opioid Prescribing Is Still High And Varies From County To County Cdc Online Newsroom Cdc
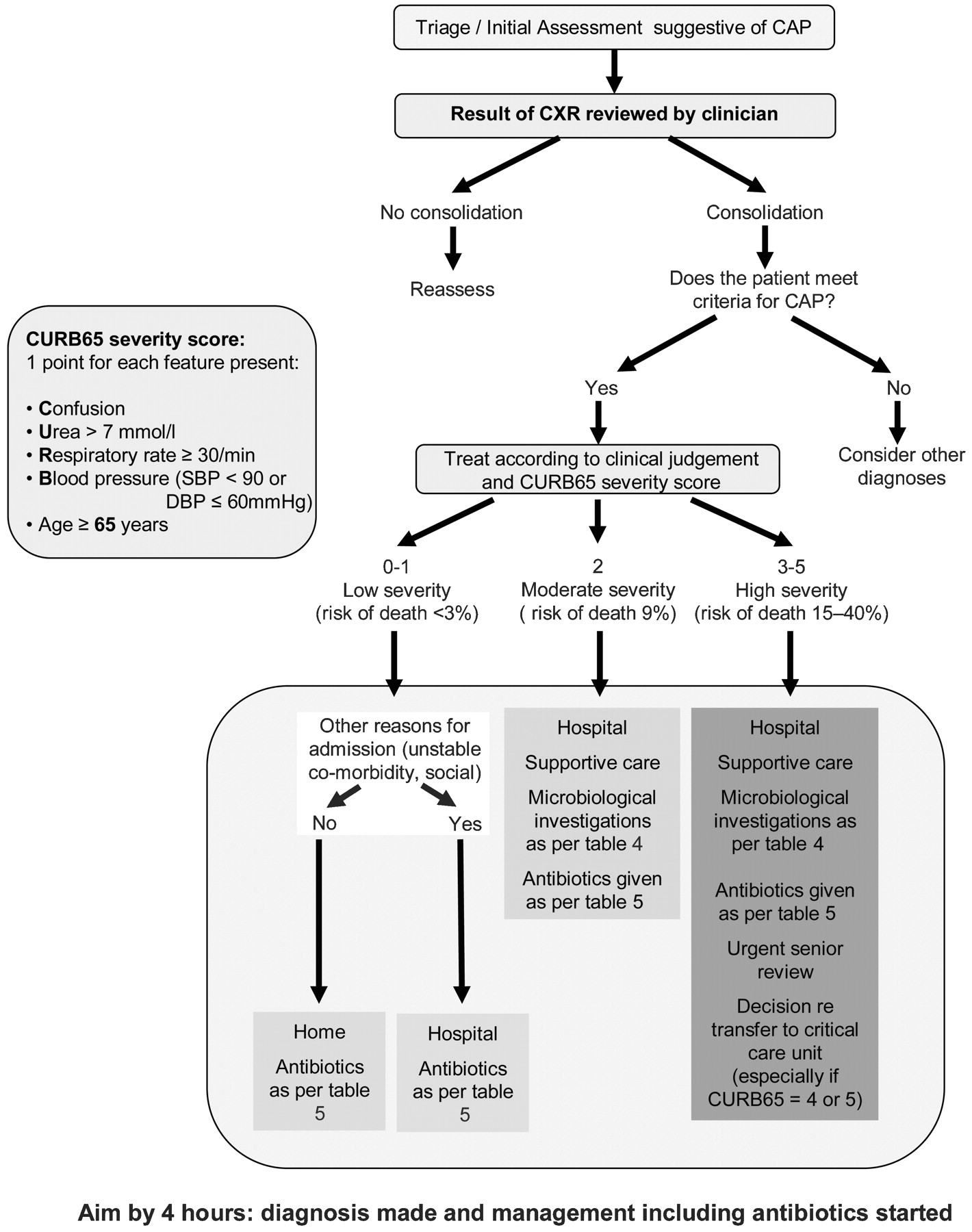
The CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain highlights twelve recommended actions that all prescribers can take to lower their patients risk of overdose.

Opioid prescribing guidelines. Opioids should be prescribed only for severe acute pain. Opioid selection dosage duration follow-up and. Recommendations focus on the use of opioids in treating chronic pain pain lasting longer than 3 months or past the time of normal tissue healing outside of active cancer.
Opioid prescribing rates started to decline in 2012 but still remain high. Opioid Prescription Tools and Trainings CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain Recommendations to help ensure patients have access to safer more effective chronic pain treatment while reducing the risk of opioid use disorder overdose and. INITIATE opioid prescribing guidelines see page 1 a Common acute pain conditions rarely indicated for opioids non-inclusive FibromyalgiaNeuropathic pain Headache Self-limited illness ie sore throat Uncomplicated back and neck pain Uncomplicated musculoskeletal pain ALGORITHM b Acute exacerbation of existing.
The CDC opioid prescribing guideline has failed to reduce addiction and overdoses significantly worsened the quality of pain care in the United States and should be revoked according to a large new survey of patients and healthcare providers by Pain News Network. The 2016 CDC guidelines for opioid prescribing by primary care physicians have exposed some shortfalls in our thinking about opioid use and stranded many chronic pain patients with inadequate analgesia. And for a limited period.
Over two-thirds believe the federal government should not have guidelines for. CDC developed and published the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain to provide recommendations for the prescribing of opioid pain medication for patients 18 and older in primary care settings. Opioids are often prescribed to help treat chronic pain.
The 2016 guideline provided recommendations for primary care clinicians who were prescribing opioids for chronic pain not including active cancer patients treatment palliative care or end of life care. Guidelines provide clinicians with ways to identify patients at risk of opioid use disorder and best practices of prescribing opioids. Prescribing guidelines were developed for opioid-naïve adult patients without chronic pain undergoing uncomplicated procedures.
When prescribing opioids physicians should consider writing two separate prescriptions for smaller amounts of opioids with specific refill dates rather than a single large prescription. If opioids are necessary they should be prescribed at the lowest effective dose. The CDC initially refused to identify who wrote the guideline or who its advisors were.
The CDCs opioid prescribing guideline has failed to reduce addiction and overdoses significantly worsened the quality of pain care in the United States and should be revoked according to a large new survey of patients and healthcare providers by Pain News Network an independent non-profit news organization. For acute pain unrelated to surgerymajor trauma providers should prescribe. Thats what researchers found in a new retrospective stu During this time the rate of opioid prescribing at discharge fell sharply.
Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain. Efforts to stop the opioid epidemic may have had an unintended consequence on pain management for near end-of-life terminally ill patients. The number of opioid tablets was defined using oxycodone 5 mg oral equivalents.
Determining when to initiate or continue opioids for chronic pain 2. Most patients do not fill the second prescription thus limiting opioid excess in a patients home and potential misuse. The CDCs opioid prescribing guideline has failed to reduce addiction and overdoses significantly worsened the quality of pain care in the United States and should be revoked according to.
The United States is in the midst of an opioid epidemic that. When the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention released the draft version of its opioid prescribing guideline in September 2015 the agency was roundly criticized for its secrecy and lack of transparency. Is intended to improve communication between providers and patients about the risks and benefits of opioid therapy for chronic pain improve the safety and effectiveness of pain treatment and reduce the risks associated with long-term opioid therapy including opioid use disorder and overdose.
In 2016 the CDC introduced the CDC Guideline for Prescribing Opioids for Chronic Pain. The Arizona Opioid Prescribing Guidelines 2018 are intended for use by clinicians in primary care and outpatient settings who provide care to patients receiving treatment for acute and chronic pain that is not occurring at the end of life or after complex surgery. There were no public hearings.
No more than a 7-day supply.





/bassinet-vs-crib-which-is-better-for-my-baby-4175857_V2-01-2b6263ba0db1433ca618a9feb0c946ca.png)