Peritoneal dialysis was first used for the management of end-stage renal disease in 1959. You or your caregiver can perform this at home.
 Pd Catheter Outflow Failure Renal Fellow Network
Pd Catheter Outflow Failure Renal Fellow Network
What is peritoneal dialysis catheter care.

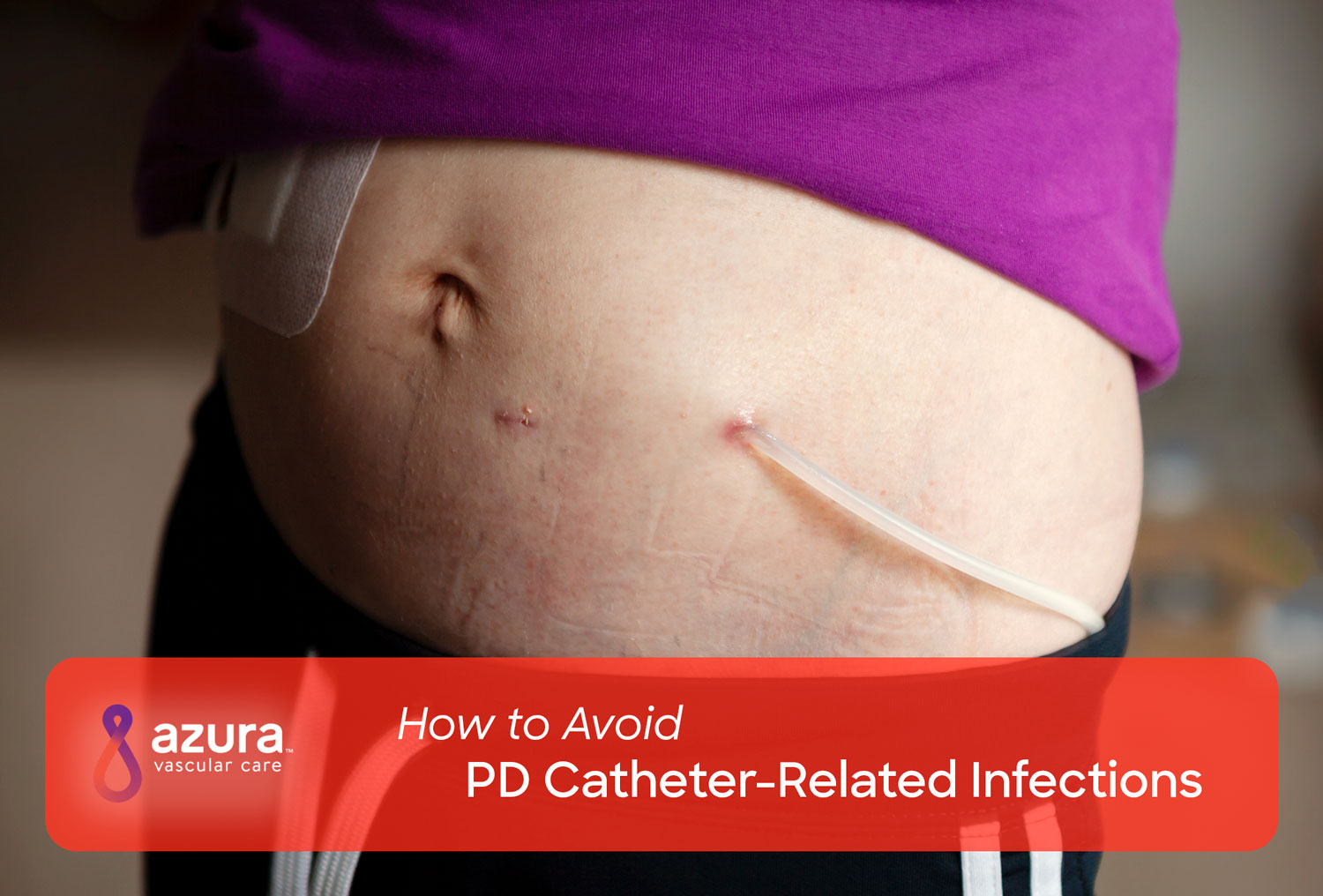
Peritoneal dialysis catheter. You will need to care for the catheter site by cleaning it and changing your bandages correctly. Peritoneal dialysis catheter obstruction is frequently caused by omentum blocking the side. Blind Seldinger technique surgical placement peritoneoscopic insertion laparoscopic approach Moncrief-Popovich technique and fluoroscopic insertion.
The incidence of omental wrapping of CAPD catheters has been reported from 45 to 15 16. Omental wrapping usually develops early after catheter placement. The catheter itself is a long thin flexible tube that is surgically placed into the abdomen directly below the belly button.
1 I In 1968 Henry Tenckhoff developed the indwelling. The PD catheter is soft to touch and should feel quite comfortable against your body. The success of peritoneal dialysis as renal-replacement therapy depends on a well-functioning peritoneal catheter.
During the planning process it is important to understand the different. Peritoneal dialysis is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the lining of your abdomen or belly to filter your blood inside your body. Peritoneal dialysis catheters are the devices used during peritoneal dialysis to bring fluid in and out of a persons abdomen.
A few weeks before you start peritoneal dialysis a surgeon places a soft tube called a catheter in your belly. Peritoneal dialysis catheter care is instruction on how to help keep the catheter working properly and to prevent infection. In a surgical procedure performed in a hospital or ambulatory surgery center the inner tip of the catheter is inserted within the patients peritoneal cavity.
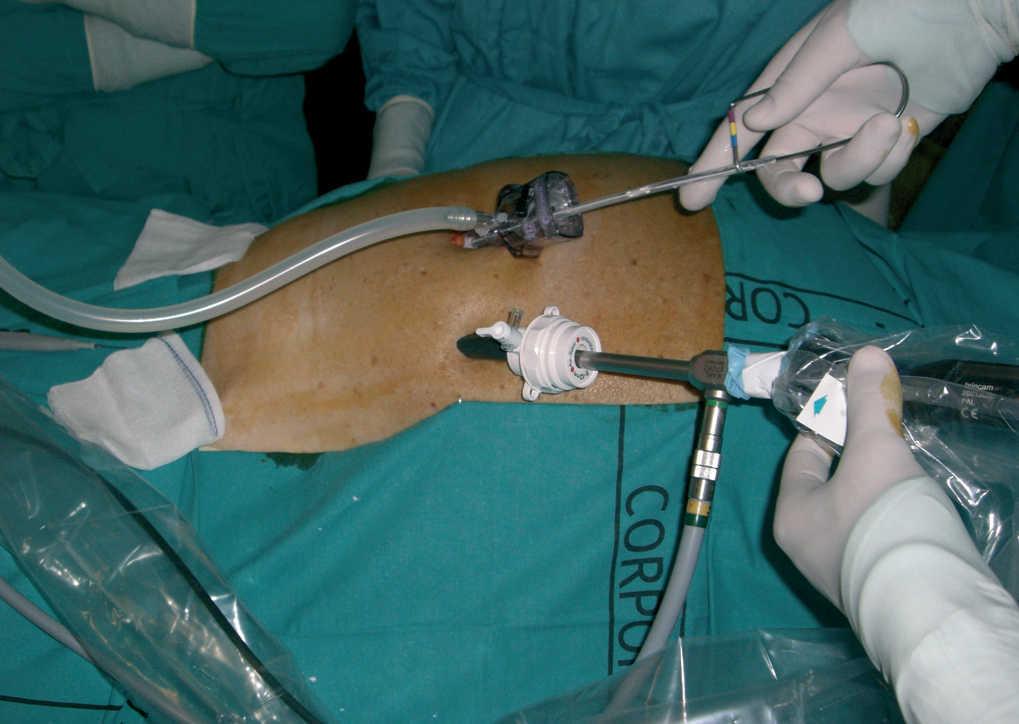
Once the catheter is surgically implanted dialysis can be performed at home by the patient based on hisher individual schedule and needs. The catheter placement procedure begins with. This would then allow you to mark the area.
Special cuffs help to keep the catheter inside your body you wont be able to feel. Knowledge of best practices in catheter insertion can minimize the risk of catheter complications that lead to peritoneal dialysis failure. A small piece of tubing is left outside of the body that can be covered when not in use.
Right After Your Catheter is Placed. The peritoneal dialysis catheter is placed through the abdomen and into the peritoneum. Holes of the catheter tubing.
A PD catheter is a flexible hollow tube about the size of a straw thats surgically placed in your lower abdomen. Peritoneal dialysis catheters are used during peritoneal kidney dialysis. While both methods are currently used for dialysis there are significant differences between a peritoneal dialysis PD catheter and a central venous catheter CVC.
Taking Care of Your Peritoneal Dialysis PD Catheter Taking good care of the PD catheter and the skin around it called the exit site is the most important way to keep the catheter working well and to lower the chance for infection. Peritoneal dialysis catheter procedures Peritoneal dialysis PD catheters may be placed into the abdominal cavity by surgeons interventional radiologists or interventional nephrologists. Hence when marking the abdomen pre-operatively one can hang the catheter against the abdominal wall such that the tip of the catheter is at the level of pubic symphisis.
Your healthcare provider will change your bandages for the first 2 weeks. Medtronic Argylecatheters are used for peritoneal dialysis in patients with renal failure. A PD catheter sometimes called a Tenckhoff catheter is a special tube that is inserted into your abdominal cavity space around the organs within your tummy.
A peritoneal dialysis catheter is the only type of access for peritoneal dialysis PD. Health care providers call this lining the peritoneum. The peritoneal dialysis catheter is the pubic symphisis.
There are several techniques. A peritoneal dialysis catheter offers the patient increased freedom and minimizes lifestyle interruptions. A sterile fluid is instilled through the catheter into your peritoneum to clean the blood inside your body.
When your kidneys fail to function properly your doctor may suggest and start planning for dialysis.