There has been tremendous progress in treatment of heart disease in children. Common causes include genetic defects eg trisomies maternal infections eg rubella or maternal use of drugs or alcohol during pregnancy.
 Acyanotic Congenital Heart Lesions Part 1 From Pedscases With Additional Resources Tom Wade Md
Acyanotic Congenital Heart Lesions Part 1 From Pedscases With Additional Resources Tom Wade Md
Acyanotic congenital heart defect were under 1 year of age while the remaining 378 were over 1 year old.

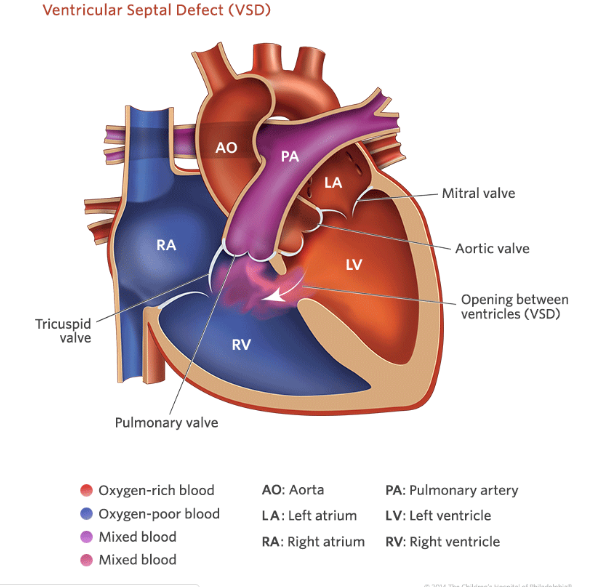
Acyanotic congenital heart disease. Discuss the possible cause of CHD. Shunt lesions such as ventricular septal defects VSDs allow oxygenated blood to bypass the systemic circulation and reenter the pulmonary circulation. Since the description of surgery for patent ductus arteriosus in late 1930s an innumerable number of advances have taken place in the management of congenital heart defects CHDs.
Gupta A Mogos C Schmer V Gudavalli M J Perinat Med 1999274292-4. Acyanotic congenital heart disease Acyanotic heart defects are congenital cardiac malformations that affect the atrial or ventricular walls heart valves or large blood vessels. Discuss the role of PDA and patent foramen ovale.
Acyanotic heart defects are congenital cardiac malformations that affect the atrial or ventricular walls heart valves or large blood vessels. Ventricular septal defect VSD atrial septal defect ASD atrioventricular septal defect. Acyanotic heart defects are congenital cardiac malformations that affect the atrial or ventricular walls heart valves or large blood vessels.
Ad Schedule a visit with a Cardiologist today in Katy. Congenital heart defects are classified into two broad categories. Common causes include genetic defects eg trisomies maternal infections eg rubella or maternal consumption of.
Acyanotic congenital heart disease comprises numerous etiologies which can be divided into those with increased pulmonary vascularity pulmonary plethora and those with normal vascularity. Although most resolve spontaneously many will remain hemodynamically significant particularly in the premature infant. Device therapy is increasingly being used in acyanotic congenital heart disease while surgical results have improved significantly to give smile to many cyanotic heart disease children and their parents.
Common causes include genetic defects eg trisomies maternal infections eg rubella or maternal consumption of drugs or alcohol during pregnancy. One day old infant with acyanotic congenital heart disease. By the end of this lecture the student should be able to.
Identify cardiovascular anatomy and function. Acyanotic and cyanotic lesions. Acyanotic congenital heart diseases or left-to-right shunting lesions are the most common form of congenital heart disease.
In this review the current status of treatment of seven of the most common acyanotic CHDs was reviewed. Severe lesions may also cause cyanosis and distress type problems in patients also. 43 Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease Marsha Ayzen Anitha S.
John Acyanotic heart lesions can be separated into two categories. Nonshunt lesions consist largely of valvular disease and aortic arch. Congenital heart Disease Objectives.
Obstructive Lesions Pulmonary Valve Stenosis with Intact Ventricular Septum Pulmonary Valve Stenosis with Intact Ventricular Septum Of the various forms of right ventricular outflow obstruction with an Intact ventricular septum the most common is isolated valvular pulmonary stenosis which accounts for 7-10 of all congenital heart defects. Acyanotic congenital heart disease ACHD can present at birth but often is seen in older children or adults unless the lesions are severe especially obstructive lesions. Growth Status of Acyanotic Congenital Heart Defect Patients The presence of congenital defect in the heart structure increase the metabolic demand and total energy expenditure of the body while reduced body mass.
Ad Schedule a visit with a Cardiologist today in Katy. Shunt lesions and nonshunt lesions. This article makes an attempt to increase awareness of general pediatricians about common congenital heart.
The most common acyanotic lesions are ventricular septal defect atrial septal defect.