To determine predictors of 5-year mortality in pulmonary Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare complex MAC disease. Overall 5-year mortality was 280.
 Pulmonary Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
Pulmonary Mycobacterium Avium Complex Infection Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
In this clinical setting MAC has.
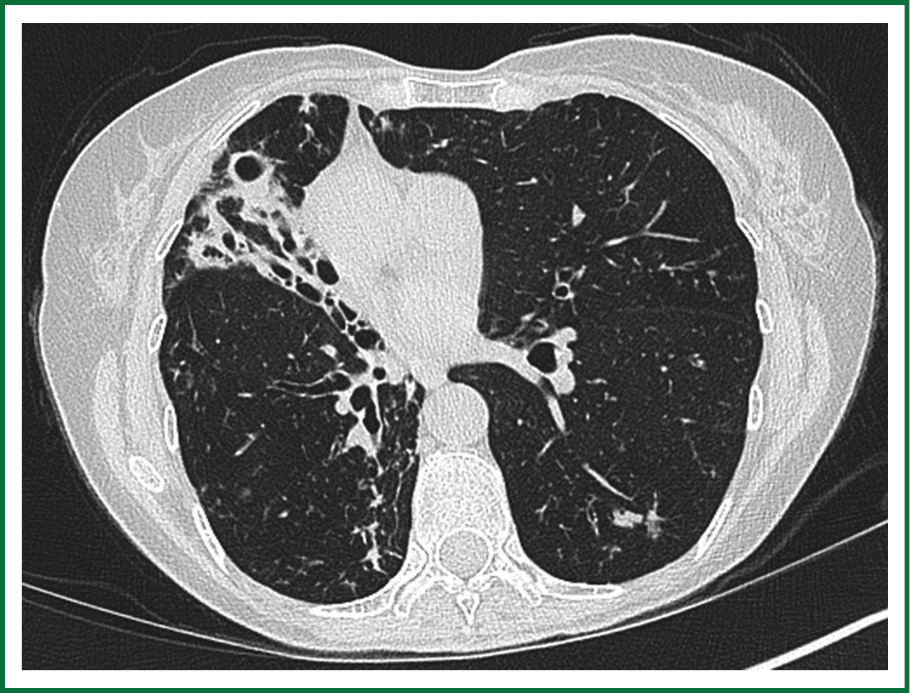
Pulmonary mac infection. Article in Japanese Kikuchi T1. For nodular disease the risk factors are being Caucasian female average age between 60 and 70 and having bronchiectasis. The clinical syndromes associated with each are clinically indistinguishable.
Mycobacterium avium complex MAC is the major pathologic nontuberculous mycobacteria causing lung disease LD in humans worldwide. MAC includes two closely related species Mycobacterium avium and Mycobacterium intracellulare and may also be referred to as MAI. Pulmonary Mycobacterium avium complex MAC infection causes chronic pulmonary diseases.
1Department of Pulmonary Medicine Tohoku University Hospital. Species in the complex include Mycobacterium avium Mycobacterium intracellulare and Mycobacterium chimaera latter recently added. MAC lung disease is an infection caused a group of bacteria called Mycobacterium avium complex MAC.
Pulmonary MAC infections affect the lungs. Pulmonary disease due to a species within MAC 12. MAC Lung Disease is acquired from the environment soil air natural waters tap water etc.
Retrospective study of 164 patients diagnosed with pulmonary MAC disease between 1999 and 2005 and followed for 5 years. This is the most common type of MAC infection and mainly affects people who have lung disease. The incidence of nontuberculous mycobacterial NTM pulmonary disease caused by Mycobacterium avium complex MAC in apparently immune-competent people is increasing worldwide.
Mycobacterium avium complex MAC infection is known to cause disseminated disease in patients with AIDS Since the advent of HAART the incidence of disseminated MAC infection has decreased dramatically Although this pathogen has been known to frequently colonize lung secretions of HIV-infected individuals to our knowledge only 20 cases of isolated pulmonary MAC infection. MAC lung disease is manifested either by fibrocavitary radiographic changes similar to pulmonary tuberculosis or by bronchiectasis with nodular and reticulonodular radiographic changes. The MAC disease in AIDS is widely disseminated throughout the body and rarely involves the lung while pulmonary MAC only involves the lungs.
Symptoms of disseminated MAC infection include. Therefore we hypothesized that MAC may be linked with a disease-susceptibility gene and determined human leukocyte-associated antigens HLA in patients with pulmonary MAC infection. Slow-growing nontuberculous mycobacteria.
We performed a systematic review of the published literature on five-year all-cause mortality in patients with MAC lung disease and pooled the mortality rates to give an overall estimate of five-year mortality. Although the burden of MAC-LD has increased over the past two decades treatment remains difficult because of intolerance of long-term antibiotics lack of adherence to guidelines and disease recurrence. Although pulmonary MAC disease tends to have variable disease progression predictors related to disease progression have not been fully established.
MAC is primarily a pulmonary pathogen that affects individuals who are immune compromised eg from AIDS hairy cell leukemia immunosuppressive chemotherapy. MAC occurs in the natural environment and the common source of infection appears to be water soil or dust with human-to-human transmission considered uncommon 13As an opportunistic pathogen MAC causes disseminated disease in immmunocompromised hosts such as individuals with HIV infection. MAC lung disease seen in HIV negative non-AIDS patients is a chronic lung infection and early-on is often misdiagnosed as chronic bronchitis or recurrent pneumonia.
The symptoms of pulmonary MAC infection start slowly get worse over time and may last for weeks to months. HLA phenotypes were tested in 59 patients with pulmonary MAC infection and diagnosed according to the criteria of the American Thoracic Society. MAC is one of a large group of nontuberculous mycobacteria NTM and the most common cause of NTM lung disease in the US.
Pulmonary MAC disease and the mycobacterial genotyping. Because pulmonary MAC infection typically causes pathological abnormalities in the more distal airways we reviewed the radiographic location of the squamous cell cancers in the MAClung cancer group looking for potential concordance with the location of MAC infection. MAC pulmonary lung disease major susceptibility risk factors depend on which of the two types of disease are present.
People with pulmonary MAC infections may experience cough weight loss fever fatigue and night sweats. This latter form of MAC lung disease termed nodular bronchiectatic NB MAC lung disease is the most common form of MAC lung disease in the United States. Among 117 patients with microbiological outcomes 54 were treated treated MAC patients and 24.





















:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Fruitarian-diet_final-4d6bd3f2bf504edd9e88125d148dab7a.png)