The authors concluded that cognitive functioning in older people with schizophrenia is different from that seen in Alzheimers disease. Schizophrenia in Elderly Patients Anees Fatima1 Uzma Barkat1 Khawaja Tahir Mahmood2 and Marriam Zaka1 1 Department of Pharmacy Lahore College for Women University Lahore Pakistan 2 Drug Testing Laboratory Government of Punjab Lahore Pakistan Abstract Schizophrenia is a severe mental illness characterized by positive and negative symptoms.
 Psychosis In The Older Patient Module 1 Thomas
Psychosis In The Older Patient Module 1 Thomas
Schizophrenia In The Elderly Schizophrenia is a chronic neuropsychiatric disorder that produces psychotic negative and disorganized symptoms.

Schizophrenia in elderly. Psychotic and disorganized symptoms are grouped together as positive symptoms. Older individuals with schizophrenia have a two-fold increased risk of developing dementia before the age of 80 years when compared with the general population. Causes and symptoms of schizophrenia in the elderly As with many mental disorders there is no exact pinpointed cause of schizophrenia but.
Schizophrenia is a psychiatric disorder of unknown etiology that typically has an onset in early adulthood and persists for the remainder of the lifespan. The remainder reside in nursing homes or as psychiatric inpatients. Older people with schizophrenia have traditionally been divided into two main groups those who develop the illness in later life and those who have had it from an early age and have now grown old.
There are multiple factors that can increase the incidence of schizophrenia in the elderly. These include changes in manifestation of schizophrenic illness in later life age-related changes in response to pharmacological treatments and psychosocial issues associated with older life status. You may not necessarily be able to reach for a full recovery for the patient but treating some of the symptoms and making life more meaningful to the patient is possible.
The prevalence of dementia in older adults with schizophrenia is expected to increase significantly. Negative symptoms include apathy affective blunting and ambivalence. Schizophrenia in the elderly population is categorized by either an early onset and middle-age or old age experienced symptoms earlyonset schizophrenia or late-onset type the disease must be.
People age 65 and older with schizophrenia comprise a small but growing number of the mentally ill that nurses especially those who work in nursing homes care for. Elderly with schizophrenia may need more help with daily living looking after themselves transportation taking care of their home etc. According to a review by Lamberti and Tariot 4 several studies have shown that the prevalence of schizophrenia in nursing homes ranges from 15 to 12 of residents.
Historically it was Kraepelin in the early 20th century who recognised that the non-affective psychosis in young adults that he called dementia praecox could also first become apparent in. The treatment of schizophrenia in older populations poses special challenges for patients family members and clinicians. These include changes in manifestation of schizophrenic illness in later.
Currently at least 85 of older people with schizophrenia live in the community. They are subject to all of the chronic and acute illnesses common to elderly. The term elderly refers to people aged 65 and older.
Neurochemical changes coming with age can also stimulate the affection not to mention the various sensory deficits cognitive problems social isolation and other age related issues. For most affected individuals the illness is recurrent with psychotic symptoms that tend to be episodic in nature. The treatment of schizophrenia in older populations poses special challenges for patients family members and clinicians.
It will be useful to briefly describe the nosology of schizophrenia in late life. Risk factors for schizophrenia in older adults include family history sensory deficits social isolation premorbid personality disorder neuropsychological abnormalities and being. Age is the most important because it underlines a common deterioration in the brains physiology.
As the data on the treatment of schizophrenia patients in that age group are very limited the term older is used here to refer to middle-aged 45-64 years and elderly 65 years patients. An early study of older in-patients with schizophrenia Reference Harvey White and Parrella Harvey 1995 demonstrated that cognitive changes were very slow over time despite low MMSE scores at initial assessment. Elderly schizophrenics are a heterogeneous group.
 Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
 Pdf Elderly Patients With Schizophrenia And Depression Diagnosis And Treatment
Pdf Elderly Patients With Schizophrenia And Depression Diagnosis And Treatment
 Schizophrenia Chapter 16 Schizophrenia L L Fascinated And
Schizophrenia Chapter 16 Schizophrenia L L Fascinated And
 Psychiatric Disorders That May Cause Psychosis In The Elderly Download Table
Psychiatric Disorders That May Cause Psychosis In The Elderly Download Table
 Schizophrenia Warning Signs And Symptoms In Elderly
Schizophrenia Warning Signs And Symptoms In Elderly
 Schizophrenia In Elderly Managing Old Age Psychotic Disorder
Schizophrenia In Elderly Managing Old Age Psychotic Disorder
 Ppt Psychosis In The Elderly Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 485039
Ppt Psychosis In The Elderly Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 485039
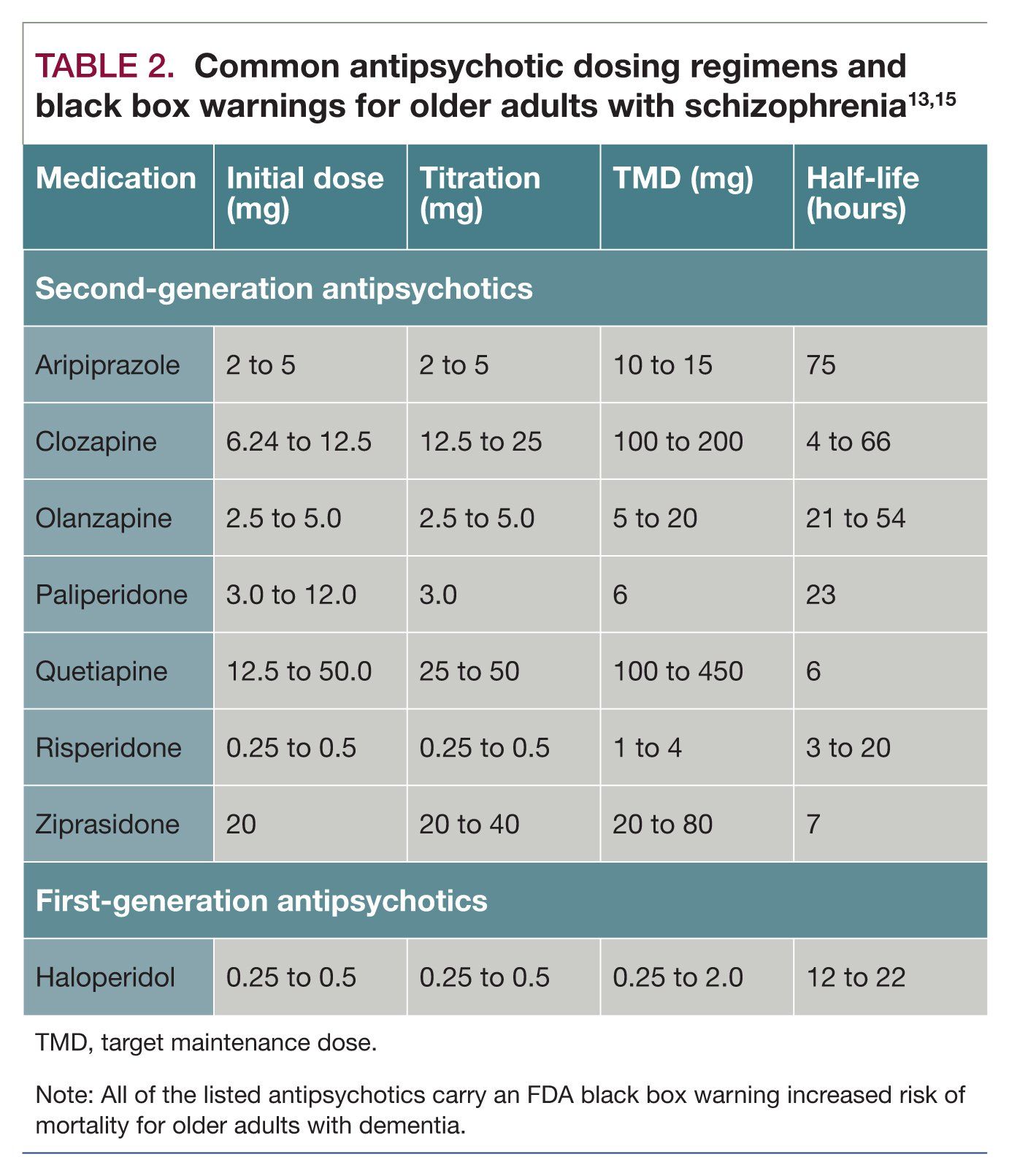 Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
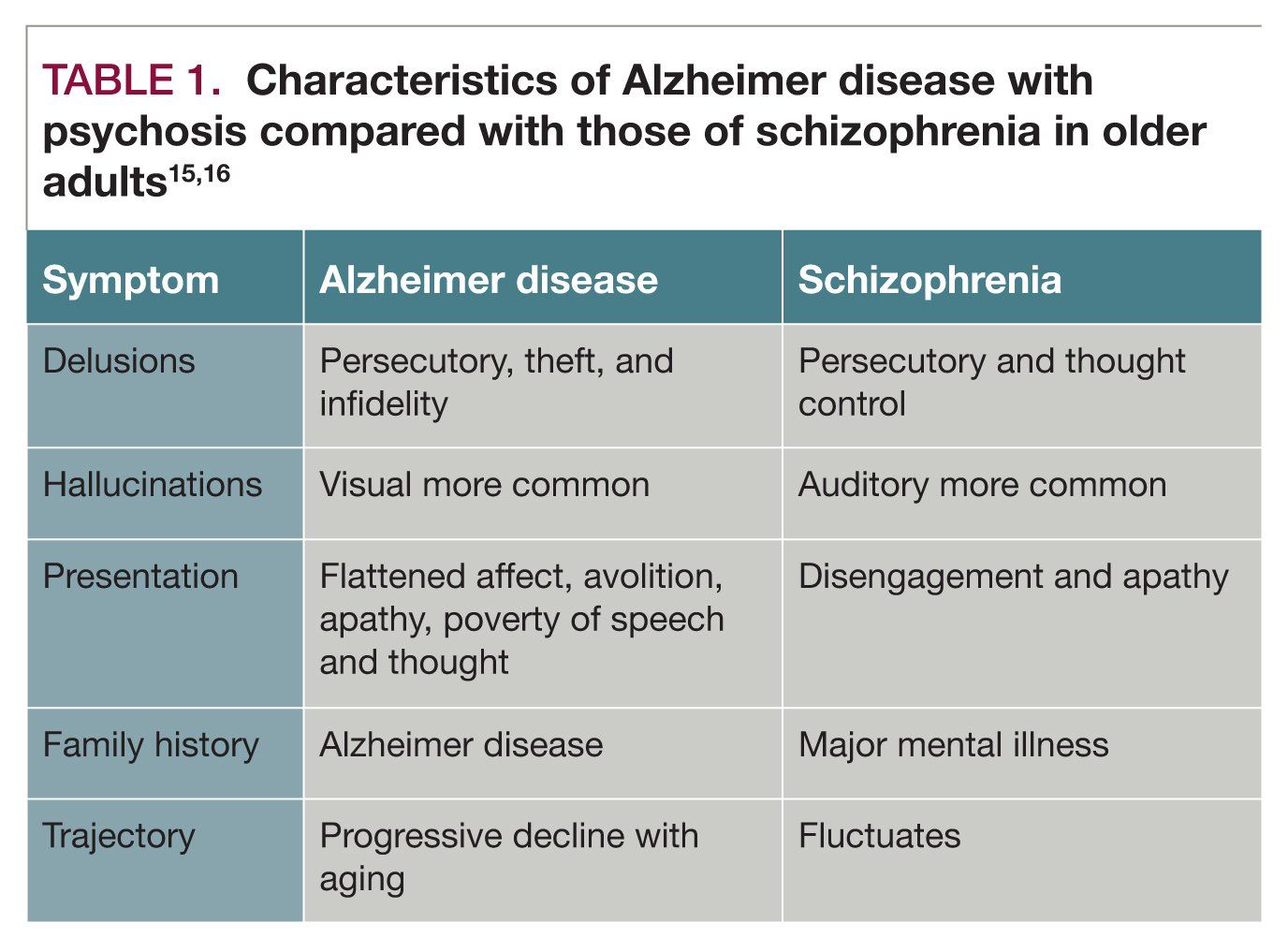 Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
 Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
Schizophrenia In Later Life Patient Characteristics And Treatment Strategies
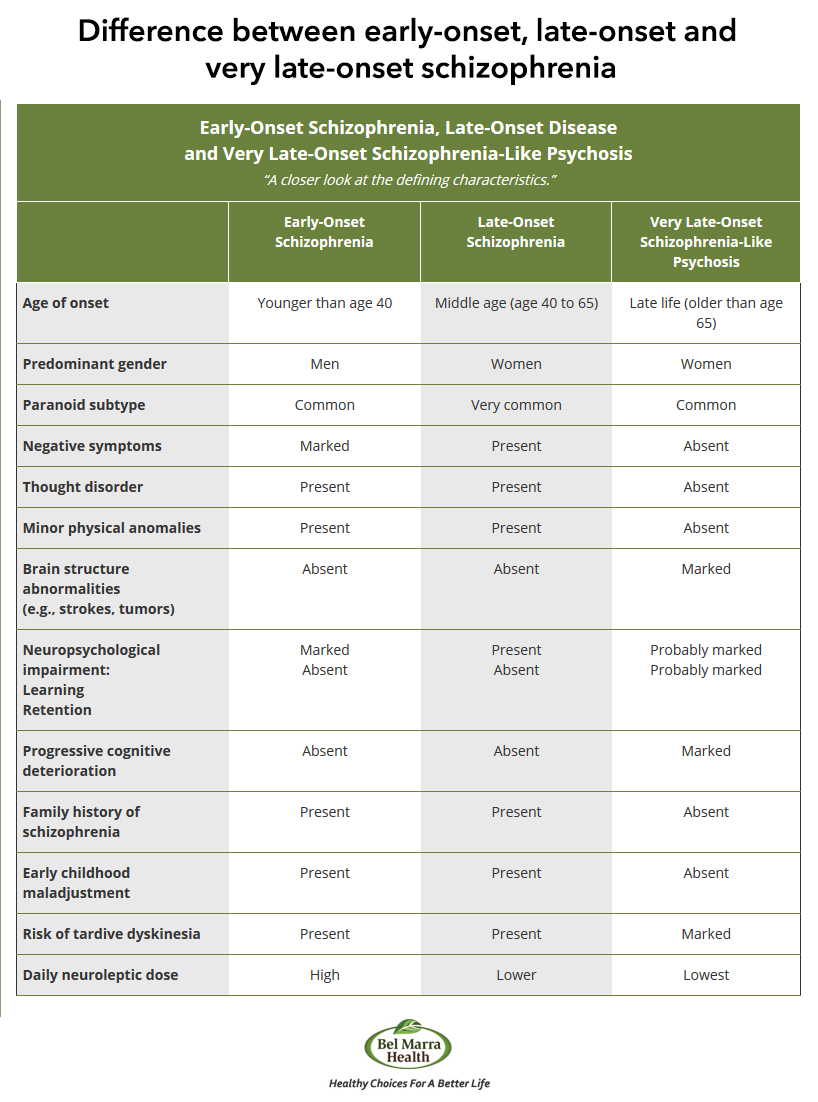 Schizophrenia In Elderly Managing Old Age Psychotic Disorder
Schizophrenia In Elderly Managing Old Age Psychotic Disorder
 6 Causes Of Paranoia In Aging Parents Checking Safety
6 Causes Of Paranoia In Aging Parents Checking Safety
 Schizophrenia In The Elderly Schiz Life
Schizophrenia In The Elderly Schiz Life

Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar
Catatan: Hanya anggota dari blog ini yang dapat mengirim komentar.